Frontend vs Backend Development: Key Differences, Skills, and Career Comparison
In the world of web development, two roles dominate the conversation: Frontend Development and Backend Development. Every website or web application you use today is built using a combination of both. While backend developers focus on logic, servers, and databases, frontend developers bring applications to life by crafting what users actually see and interact with.
This blog explores frontend vs backend development, their differences, required skills, tools, career paths, and why frontend development often feels more rewarding and visible—especially in today’s user-experience-driven digital landscape.
What Is Frontend Development?
Frontend development refers to building the client-side of a website or application—the part users directly see and interact with in their browsers.
Everything from:
-
Layout and colors
-
Buttons and forms
-
Animations and transitions
-
Responsive design
is handled by frontend developers.
A frontend developer’s main goal is to deliver a smooth, fast, and visually appealing user experience across devices and browsers.
Core Frontend Technologies
-
HTML – Structure of the web
-
CSS – Styling and layout
-
JavaScript – Interactivity and logic
Modern frontend developers also use frameworks and libraries like React, Vue, and Next.js to build scalable applications.
What Is Backend Development?
Backend development focuses on the server-side of applications. It handles everything users don’t directly see but heavily depend on.
Backend responsibilities include:
-
Server logic
-
Authentication and authorization
-
Database operations
-
APIs and data processing
-
Performance and security
Backend developers ensure that data flows correctly between the frontend and databases.
Core Backend Technologies
-
Languages: Node.js, Python, Java, PHP
-
Databases: MongoDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL
-
Servers: Express, Django, Spring Boot
-
Authentication: JWT, OAuth
Frontend vs Backend: Key Differences
| Feature | Frontend Development | Backend Development |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | User Interface & UX | Business Logic & Data |
| Visibility | Highly visible to users | Mostly hidden |
| Technologies | HTML, CSS, JS, React | Node.js, Python, Databases |
| Creativity | High (design + logic) | More logic-focused |
| Feedback | Instant visual feedback | Often indirect |
| Learning Curve | Easier to start | More complex initially |
While both roles are essential, frontend development often feels more engaging, especially for developers who enjoy seeing immediate results.
Skill Comparison: Frontend vs Backend
Frontend Developer Skills
-
Responsive design principles
-
Browser compatibility
-
State management
-
Performance optimization
-
Accessibility (a11y)
-
UI/UX understanding
Backend Developer Skills
-
Database design
-
API architecture
-
Authentication & security
-
Server optimization
-
Scalability
Frontend developers must balance technical skills with design sensibility, which makes the role both challenging and creative.
Why Frontend Development Often Stands Out
While backend developers build the foundation, frontend developers define the user’s experience. A powerful backend is useless if the frontend is slow, confusing, or unattractive.
Reasons Frontend Has an Edge:
-
Immediate Visual Impact
You instantly see the result of your work in the browser. -
User-Centered Work
Frontend developers directly influence how users feel about a product. -
High Demand in Modern Apps
With React, SPAs, and PWAs, frontend roles are in massive demand. -
Creative Freedom
Animations, layouts, interactions—frontend blends creativity with logic. -
Better Personal Branding
Frontend developers can showcase portfolios, UI demos, and live projects.
Career Opportunities: Frontend vs Backend
Both roles offer strong career paths, but frontend development has expanded rapidly due to modern frameworks and design-focused products.
Frontend Career Roles
-
Frontend Developer
-
UI Engineer
-
React Developer
-
Web Performance Engineer
-
Frontend Architect
Backend Career Roles
-
Backend Developer
-
API Developer
-
Database Engineer
-
System Architect
Many developers eventually become Full Stack Developers, but frontend expertise often helps developers stand out early in their careers.
Salary Comparison
Salaries vary by region and experience, but frontend developers with modern skills are now equally competitive.
-
Frontend Developer (India): ₹4–12 LPA
-
Backend Developer (India): ₹5–14 LPA
-
Frontend Developer (Global): $70k–120k
-
React / Next.js Specialists: Often higher
Frontend developers skilled in performance optimization, accessibility, and modern frameworks can command top salaries.
Learning Curve: Which Is Easier to Start?
For beginners, frontend development is generally easier to start.
-
You can build something visible within days
-
No server or database setup initially
-
Faster motivation due to visual results
Backend development requires deeper understanding of:
-
Servers
-
Databases
-
Architecture
-
Security
This is why many developers start with frontend and later explore backend.
Frontend vs Backend: Which Should You Choose?
Choose Frontend Development if you:
-
Enjoy visual design and creativity
-
Like instant feedback
-
Want to work closely with users
-
Enjoy UI/UX and animations
Choose Backend Development if you:
-
Prefer logic-heavy work
-
Enjoy databases and systems
-
Like solving complex data problems
If you want the best of both worlds, Full Stack Development is the answer—but frontend remains the most engaging entry point.
Future Scope of Frontend vs Backend
Frontend development is evolving rapidly with:
-
AI-assisted UI generation
-
Server-side rendering (Next.js)
-
Web animations & micro-interactions
-
Accessibility-first design
Backend development remains stable, but frontend innovation is happening at a faster pace due to growing user expectations.
Conclusion
The debate of frontend vs backend development doesn’t have a single winner—both are critical for modern applications. However, frontend development has a unique advantage: it directly shapes the user experience.
With rising demand, creative freedom, visible impact, and powerful frameworks like React and Next.js, frontend development is not just coding—it’s crafting digital experiences.
If you enjoy building things people can see, feel, and interact with, frontend development is the more exciting and future-forward choice.
Master Web Development in 2026
A practical, project-based guide to modern JavaScript, React, and full-stack development. Includes 50 real-world exercises and downloadable code.
- 500+ pages of step-by-step tutorials
- Full-stack project: From idea to deployment
- Free updates & companion videos
Frontend Developer: Skills, Tools, Career Path & Future Scope
Frontend Developer: Skills, Tools, Career Path & Future Scope
In today’s digital world, Frontend Developers play a crucial role in shaping how users interact with websites and web applications. Every button you click, every animation you see, and every form you fill out is crafted by a frontend developer. As businesses move online, the demand for skilled frontend developers continues to grow rapidly.
This blog will cover what a frontend developer is, key skills, tools and technologies, career opportunities, and future trends, making it a complete SEO-friendly guide for beginners and professionals alike.
Who Is a Frontend Developer?
A Frontend Developer is responsible for building the visual and interactive parts of a website or web application. They work on the client side, meaning everything users see and interact with in their browser.
Frontend developers convert design mockups (from tools like Figma or Adobe XD) into responsive, fast, and user-friendly interfaces using code. Their main goal is to ensure a smooth and engaging user experience across all devices.
Core Responsibilities of a Frontend Developer
A frontend developer’s daily tasks include:
-
Developing responsive website layouts
-
Writing clean, maintainable, and reusable code
-
Optimizing web performance and loading speed
-
Ensuring cross-browser compatibility
-
Implementing UI/UX designs accurately
-
Fixing bugs and improving user experience
-
Collaborating with backend developers and designers
Essential Skills for a Frontend Developer
1. HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
HTML is the backbone of web pages. A frontend developer must understand semantic HTML, accessibility, and proper document structure.
SEO Tip: Semantic HTML improves search engine visibility.
2. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
CSS is used to style websites. Modern frontend developers use:
-
Flexbox & Grid
-
Responsive design
-
Animations & transitions
-
Preprocessors like SCSS
Frameworks like Tailwind CSS, Bootstrap, and DaisyUI help speed up development.
3. JavaScript
JavaScript makes websites interactive. Core concepts include:
-
DOM manipulation
-
ES6+ features
-
Promises & async/await
-
Event handling
JavaScript is the most important skill for a frontend developer.
Popular Frontend Frameworks & Libraries
React.js
React is the most widely used frontend library. It allows developers to build fast and scalable user interfaces using components.
Vue.js
Vue is beginner-friendly and flexible, popular for smaller to medium projects.
Angular
Angular is a full-fledged framework used in enterprise-level applications.
SEO Keyword: frontend developer skills, frontend frameworks
Tools Every Frontend Developer Should Know
-
Version Control: Git & GitHub
-
Package Managers: npm, yarn
-
Build Tools: Vite, Webpack
-
Design Tools: Figma, Adobe XD
-
Testing Tools: Jest, Cypress
-
Browser DevTools: Chrome DevTools
These tools improve productivity and code quality.
Frontend Developer vs Backend Developer
| Frontend Developer | Backend Developer |
|---|---|
| Works on UI/UX | Works on server logic |
| Uses HTML, CSS, JS | Uses Node.js, Python, Java |
| Focuses on user interaction | Focuses on databases & APIs |
Many developers later become Full Stack Developers by learning both.
Career Path of a Frontend Developer
A typical frontend developer career path looks like this:
-
Junior Frontend Developer
-
Frontend Developer
-
Senior Frontend Developer
-
Lead Frontend Engineer / UI Architect
With experience, you can also move into roles like:
-
UI/UX Engineer
-
Full Stack Developer
-
Technical Lead
-
Product Engineer
Salary of a Frontend Developer
Frontend developer salaries vary based on location, experience, and skills.
-
India: ₹4–12 LPA
-
USA: $70,000–120,000 per year
-
Remote Jobs: Highly competitive and well-paid
React, performance optimization, and accessibility skills can significantly increase salary.
How to Become a Frontend Developer
Follow these steps to start your frontend developer journey:
-
Learn HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
-
Practice building responsive websites
-
Learn a framework like React
-
Build real-world projects
-
Create a strong portfolio website
-
Contribute to open-source projects
-
Apply for internships and jobs
Consistency and hands-on practice are key.
Future Scope of Frontend Development
Frontend development is evolving rapidly. Future trends include:
-
AI-powered UI development
-
Web performance optimization
-
Progressive Web Apps (PWA)
-
Server-side rendering (Next.js)
-
Accessibility-first development
The demand for frontend developers is expected to grow as businesses focus more on user experience.
Why Frontend Development Is a Great Career Choice
-
High demand across industries
-
Creative and technical work
-
Remote job opportunities
-
Continuous learning and growth
-
Strong community support
Frontend development combines creativity with logic, making it an exciting career option.
Conclusion
A Frontend Developer is the bridge between design and technology. With the right skills, tools, and mindset, frontend development offers a rewarding and future-proof career. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, continuously improving your skills and staying updated with modern frameworks will help you stand out in this competitive field.
If you want to build beautiful, fast, and user-friendly web applications, frontend development is the perfect path for you.
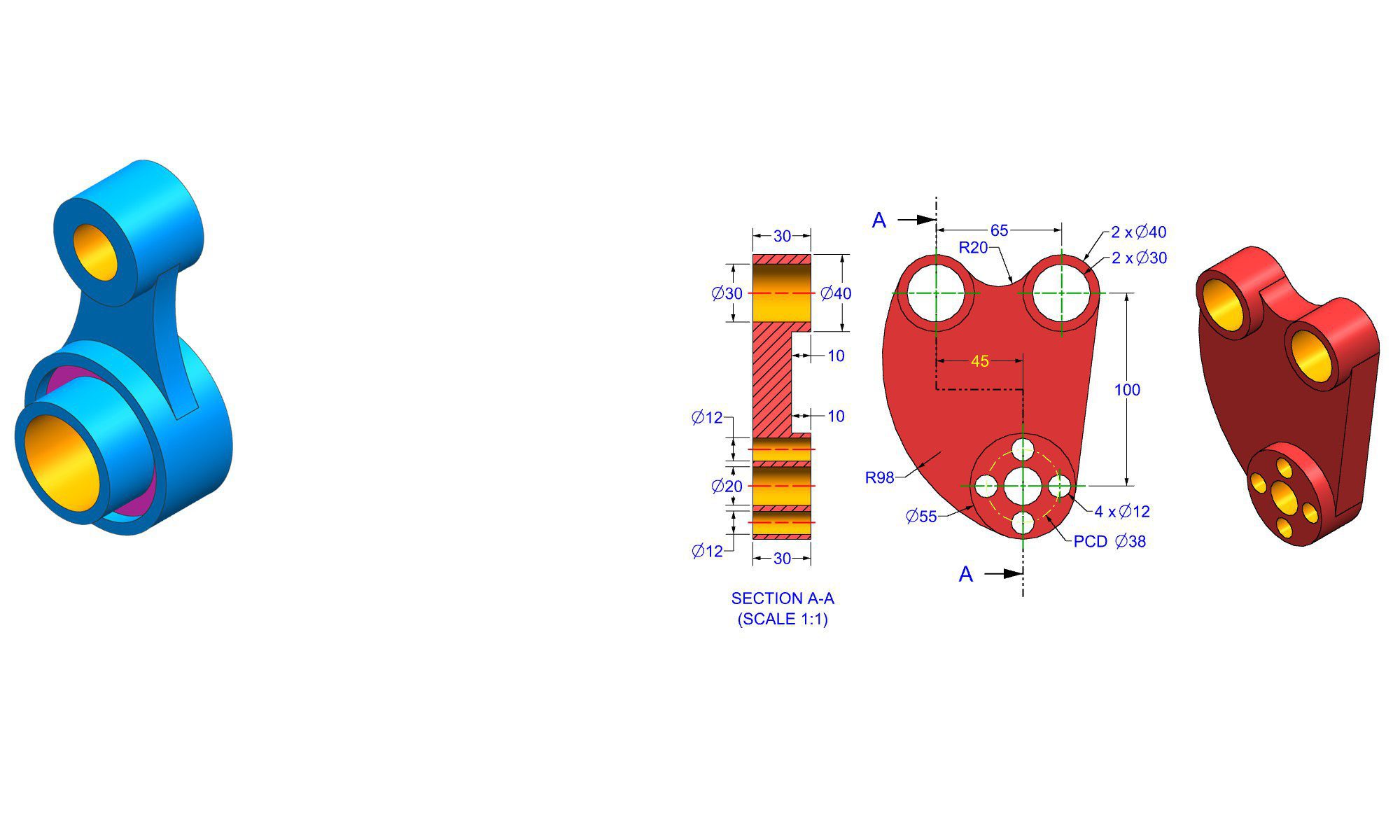
How to Use Fusion 360 – Complete Beginner Guide (2025)
How to Use Fusion 360 – Complete Beginner Guide (2025)
How to Use Fusion 360: A Complete Beginner’s Guide (2025)
Fusion 360 is one of the most powerful and beginner-friendly CAD/CAM/CAE tools available today. Developed by Autodesk, Fusion 360 is widely used for 3D modeling, product design, mechanical engineering, CNC machining, and 3D printing. Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or professional designer, learning Fusion 360 can significantly boost your design and manufacturing skills.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to use Fusion 360 step by step, from setting up your workspace to creating your first 3D model and exporting it for manufacturing.
What Is Fusion 360?
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based 3D CAD, CAM, and CAE software that combines design, engineering, and manufacturing tools in one platform. Unlike traditional CAD software, Fusion 360 allows parametric modeling, direct modeling, simulation, and collaboration in a single workflow.
Key Features of Fusion 360
-
Parametric & direct 3D modeling
-
Sketch-based design
-
Assembly & joint system
-
Simulation & stress analysis
-
CAM for CNC machining
-
Cloud collaboration & version control
How to Download and Install Fusion 360
Before learning how to use Fusion 360, you need to install it properly.
Steps to Install Fusion 360
-
Visit the Autodesk Fusion 360 official website
-
Sign in with your Autodesk account
-
Choose the correct license:
-
Personal Use (Free for hobbyists)
-
Student/Educational License
-
Commercial License
-
-
Download and install Fusion 360
-
Launch the software and sign in
Once installed, Fusion 360 automatically updates via the cloud.
Understanding the Fusion 360 Interface
When you open Fusion 360, the interface may feel overwhelming, but it’s well organized.
Main Areas of Fusion 360
-
Toolbar – Design, Solid, Surface, Mesh, and Sheet Metal tools
-
Browser Panel – Shows sketches, bodies, components, and timelines
-
Canvas – Main workspace where you model
-
Timeline – Tracks design history and parametric changes
Understanding the timeline is crucial, as it allows you to edit any step later without breaking your model.
Creating Your First Sketch in Fusion 360
Sketching is the foundation of all 3D models in Fusion 360.
Steps to Create a Sketch
-
Click Create Sketch
-
Select a plane (XY, YZ, or XZ)
-
Use sketch tools like:
-
Line
-
Rectangle
-
Circle
-
Arc
-
-
Apply dimensions (D key) to fully constrain the sketch
-
Finish the sketch
💡 Tip: Always aim for a fully constrained sketch (black lines), which ensures stability.
Turning a Sketch into a 3D Model
Once your sketch is ready, you can convert it into a solid body.
Common 3D Modeling Tools
-
Extrude (E) – Create 3D shapes from sketches
-
Revolve – Rotate a profile around an axis
-
Loft – Blend shapes between profiles
-
Sweep – Extrude along a path
Example:
-
Select a sketch profile
-
Press E (Extrude)
-
Enter distance
-
Click OK
You now have your first 3D model in Fusion 360.
Using Components and Assemblies
Fusion 360 uses a component-based workflow, which is essential for real-world designs.
Why Use Components?
-
Better organization
-
Easier assemblies
-
Motion simulation
-
Improved performance
How to Create Components
-
Right-click in the Browser
-
Select New Component
-
Model parts inside components
-
Use Joints to connect parts
This approach is ideal for mechanical designs and product assemblies.
Applying Materials and Appearance
Fusion 360 allows you to add realistic materials to your model.
Steps to Apply Materials
-
Press A (Appearance)
-
Choose a material (metal, plastic, wood, etc.)
-
Drag and drop onto your model
-
Adjust color, texture, and finish
This is useful for rendering, presentations, and client previews.
Rendering and Visualization
Fusion 360 includes a powerful rendering engine.
Rendering Workflow
-
Switch to Render Workspace
-
Set environment and lighting
-
Choose materials
-
Adjust camera angle
-
Click Render
You can render locally or use cloud rendering for faster results.
Exporting Files for Manufacturing
Fusion 360 supports multiple export formats depending on your use case.
Common Export Formats
-
STL – 3D printing
-
STEP / IGES – CAD file sharing
-
DXF – Laser cutting / CNC
-
G-code – CNC machining (CAM workspace)
To export:
-
Go to File → Export
-
Choose format
-
Save locally or to the cloud
Tips to Learn Fusion 360 Faster
-
Learn keyboard shortcuts (E, D, L, P)
-
Use parametric design properly
-
Name sketches and components
-
Watch Autodesk tutorials
-
Practice real-world projects
-
Avoid editing bodies directly—edit sketches instead
Final Thoughts
Fusion 360 is an all-in-one design and manufacturing solution that is both beginner-friendly and industry-ready. By mastering sketches, parametric modeling, components, and exporting workflows, you can design professional-grade products efficiently.
Whether you want to create mechanical parts, 3D printable models, or CNC-ready designs, Fusion 360 gives you everything you need in one powerful platform.