Introduction to AutoCAD
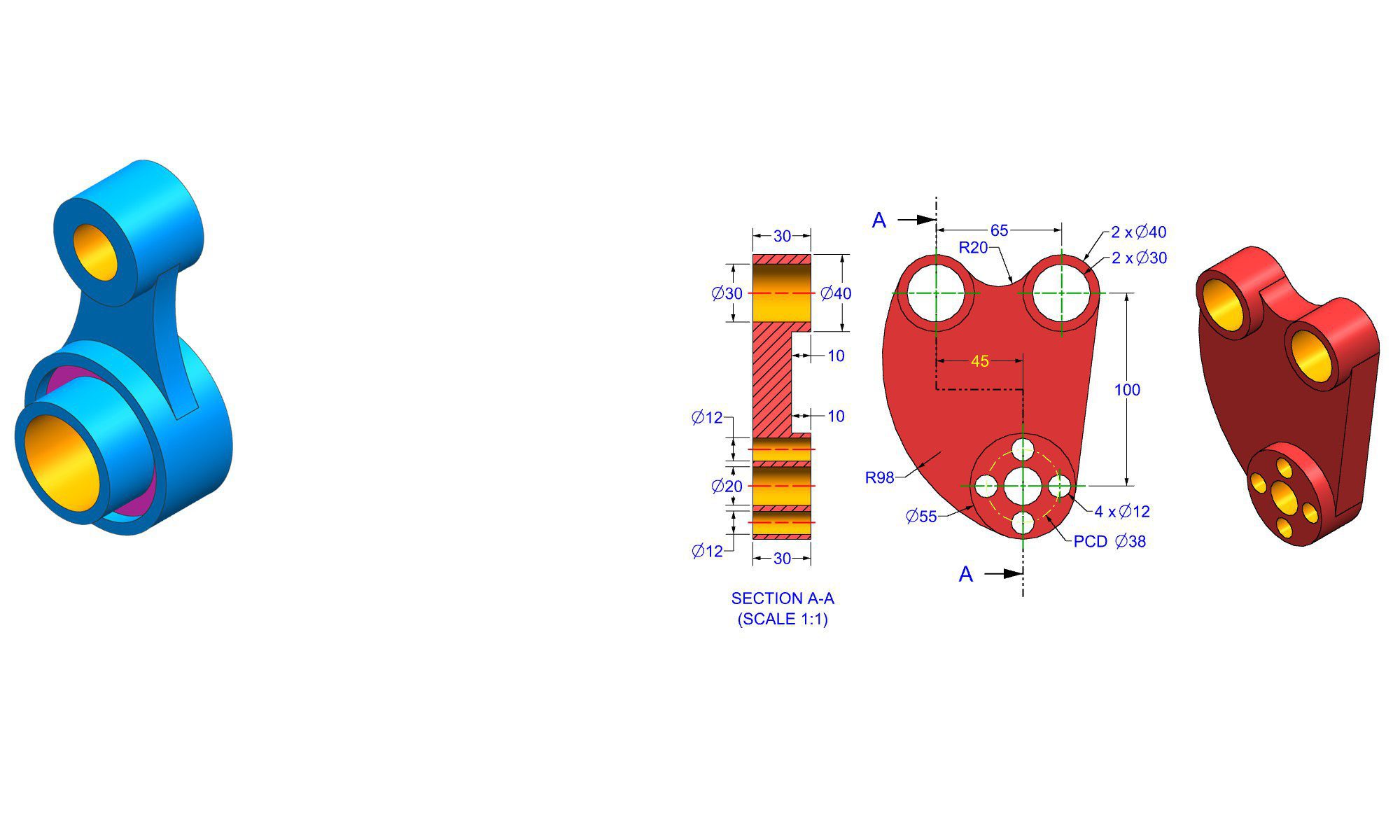
AutoCAD is one of the most popular and widely used computer-aided design (CAD) software in the world. Developed by Autodesk, AutoCAD allows professionals to create precise 2D drawings and 3D models used across industries such as architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, and interior design.
Since its launch in 1982, AutoCAD has become an industry standard for digital drafting. Whether you are a student, a beginner, or a working professional, learning AutoCAD can significantly improve your design efficiency and career prospects.
What Is AutoCAD?
AutoCAD is a professional drafting and design software that enables users to create accurate technical drawings. It replaces traditional hand-drawn blueprints with digital files that are easy to edit, share, and store.
AutoCAD supports:
-
2D drafting for floor plans, layouts, and schematics
-
3D modeling for visualization and prototyping
-
Annotation and dimensioning for technical accuracy
Its flexibility makes it suitable for both simple drawings and complex engineering projects.
Key Features of AutoCAD
AutoCAD offers a wide range of powerful tools that help designers work faster and smarter.
1. Precision Drafting Tools
AutoCAD provides exact measurement tools, snap features, grids, and coordinate systems that ensure high accuracy in every drawing.
2. 2D and 3D Capabilities
You can create detailed 2D drawings or move into 3D modeling with solid, surface, and mesh tools.
3. Customization and Automation
With AutoLISP, scripts, and macros, users can automate repetitive tasks and customize workflows to suit their needs.
4. Layer Management
Layers help organize drawings efficiently by separating elements like electrical, plumbing, dimensions, and annotations.
5. File Compatibility
AutoCAD supports multiple file formats such as DWG, DXF, PDF, and more, making collaboration easy.
Uses of AutoCAD in Different Industries
AutoCAD is used across many professional fields due to its versatility.
Architecture
Architects use AutoCAD to create:
-
Floor plans
-
Elevations
-
Sections
-
Site layouts
It helps in precise space planning and construction documentation.
Civil and Mechanical Engineering
Engineers rely on AutoCAD for:
-
Structural drawings
-
Machine parts
-
Assembly layouts
-
Infrastructure planning
Its accuracy ensures designs meet technical standards.
Interior Design
Interior designers use AutoCAD for:
-
Furniture layouts
-
Lighting plans
-
Material detailing
-
Client presentations
Manufacturing and Product Design
AutoCAD is used for designing tools, components, and prototypes before production begins.
Advantages of Using AutoCAD
There are many reasons why AutoCAD remains relevant even today.
-
High Accuracy: Eliminates manual drafting errors
-
Time-Saving: Faster revisions and edits
-
Professional Standard: Accepted worldwide
-
Scalability: Suitable for small and large projects
-
Strong Community: Large user base and learning resources
AutoCAD vs Other CAD Software
While there are many CAD tools available today, AutoCAD still stands out.
| Feature | AutoCAD | Other CAD Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Industry Acceptance | Very High | Medium |
| Learning Resources | Extensive | Limited |
| Customization | Advanced | Varies |
| Precision | Excellent | Good |
AutoCAD is often preferred for drafting, while other tools like Fusion 360 or SolidWorks are used more for parametric 3D modeling.
Learning AutoCAD: Beginner to Advanced
Learning AutoCAD is easier than ever thanks to online resources.
Best Ways to Learn AutoCAD
-
Online tutorials and video courses
-
Autodesk official documentation
-
Practice projects and real-world drawings
-
Certification programs
Skills You Need
-
Basic technical drawing knowledge
-
Understanding of dimensions and scale
-
Practice with commands and shortcuts
With consistent practice, beginners can become job-ready within a few months.
Career Opportunities with AutoCAD Skills
AutoCAD skills open doors to many career paths.
Popular job roles include:
-
AutoCAD Draftsman
-
Architectural Designer
-
Civil Engineer
-
Mechanical Design Engineer
-
Interior Designer
Freelancers with AutoCAD expertise can also work on international projects and earn competitive income.
Why AutoCAD Is Still Relevant in 2025
Despite the rise of modern 3D and BIM tools, AutoCAD remains essential because:
-
Many industries still rely on 2D drawings
-
Legacy projects are built in AutoCAD
-
It integrates well with newer software
-
It is cost-effective for drafting work
AutoCAD continues to evolve with cloud features, mobile apps, and automation tools.
Conclusion
AutoCAD is more than just drafting software—it is a foundational tool in the world of design and engineering. Its precision, flexibility, and industry acceptance make it an essential skill for students and professionals alike.
Whether you want to design buildings, create mechanical parts, or start a career in CAD drafting, AutoCAD provides the tools and opportunities to succeed. Learning AutoCAD today is an investment that can shape a strong and future-proof career.
Master Web Development in 2026
A practical, project-based guide to modern JavaScript, React, and full-stack development. Includes 50 real-world exercises and downloadable code.
- 500+ pages of step-by-step tutorials
- Full-stack project: From idea to deployment
- Free updates & companion videos