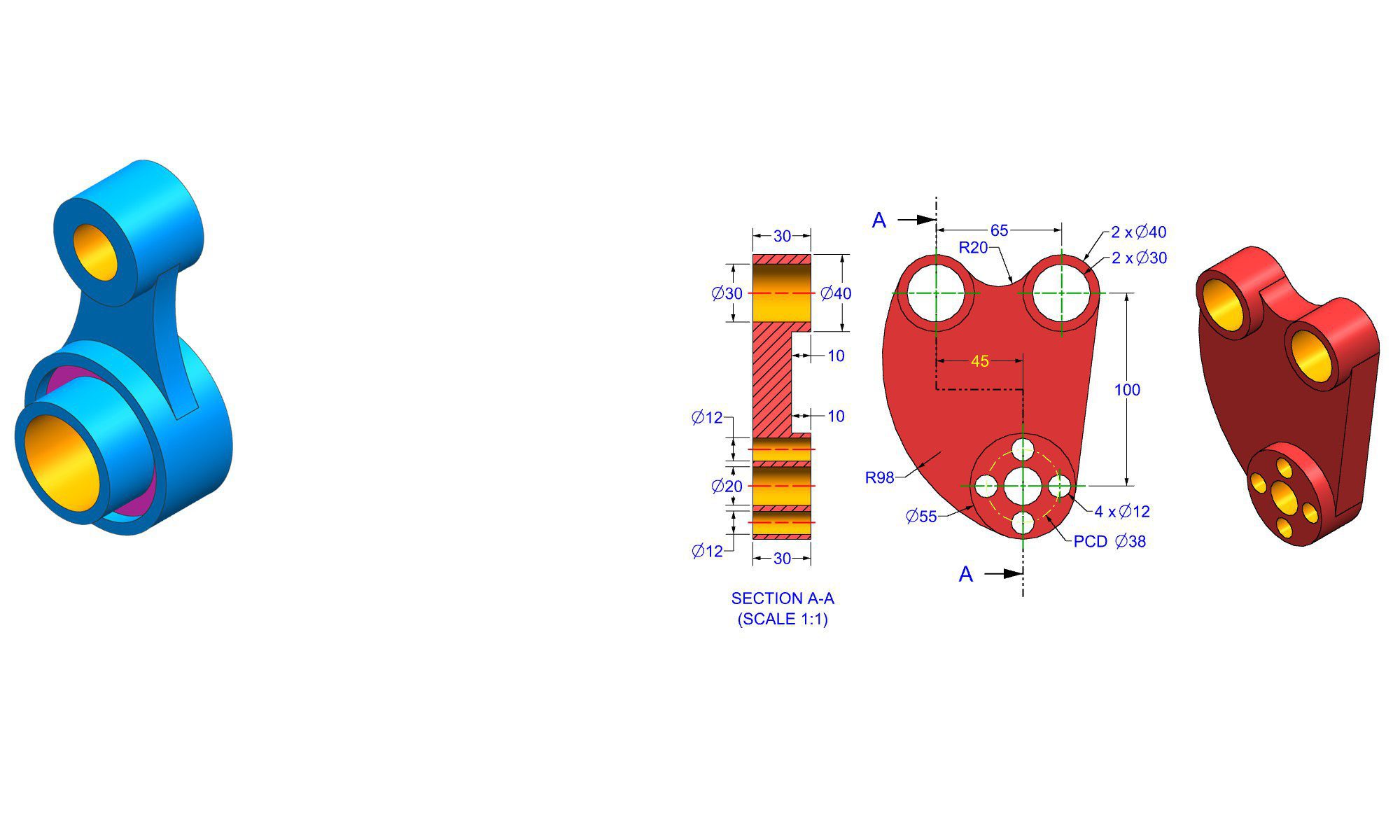
Introduction to Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is a technology that uses computer systems to assist in the creation, modification, analysis, and optimization of designs. CAD has become an essential tool across industries such as engineering, architecture, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and product design. What once required hours of manual drafting can now be completed in minutes with extreme precision.
With the rise of digital transformation, CAD has evolved from simple 2D drawings to highly advanced 3D parametric and simulation-based modeling systems. Today, CAD is not just a design tool—it is the foundation of modern engineering workflows.
What is CAD and How Does It Work?
CAD software allows designers to create accurate drawings and models using digital tools. These designs can be two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D), depending on project requirements.
At its core, CAD works by:
-
Defining geometry using mathematical equations
-
Allowing parametric control over dimensions and features
-
Enabling real-time editing and visualization
-
Supporting simulations and performance analysis
Modern CAD systems integrate with CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) and CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering), creating a complete digital product development ecosystem.
Types of CAD Systems
1. 2D CAD
2D CAD is primarily used for drafting and documentation. It replaces manual drawing boards with digital drafting tools. Applications include floor plans, electrical diagrams, and mechanical schematics.
Examples:
-
AutoCAD (2D drafting)
-
LibreCAD
2. 3D CAD
3D CAD allows designers to build realistic models with depth, volume, and mass properties. These models can be rotated, analyzed, and tested virtually.
Examples:
-
Fusion 360
-
SolidWorks
-
CATIA
-
Creo
3. Parametric CAD
Parametric CAD enables designers to define relationships between features. Changing one dimension automatically updates the entire model, ensuring design consistency.
Key Benefits of Computer-Aided Design
1. Increased Accuracy
CAD eliminates many errors caused by manual drafting. Designs are created with mathematical precision, ensuring higher quality and fewer mistakes.
2. Faster Design Process
Design iterations that once took days can now be completed in hours. CAD allows quick modifications without starting from scratch.
3. Improved Visualization
3D CAD models help designers and stakeholders visualize the final product before manufacturing begins.
4. Cost Efficiency
By detecting design flaws early, CAD reduces material waste and costly manufacturing errors.
5. Easy Collaboration
CAD files can be shared globally, enabling teams to collaborate across locations using cloud-based CAD platforms.
Applications of CAD Across Industries
Engineering and Manufacturing
CAD is widely used in mechanical, electrical, and civil engineering for product design, tooling, and production planning.
Architecture and Construction
Architects use CAD to create detailed building layouts, elevations, and 3D walkthroughs.
Automotive and Aerospace
Complex assemblies, aerodynamic simulations, and precision components rely heavily on advanced CAD tools.
Product and Industrial Design
From consumer electronics to furniture, CAD helps designers bring ideas to life with speed and creativity.
Healthcare and Biomedical
CAD is used to design prosthetics, implants, and medical devices with high accuracy.
Popular CAD Software Tools
Some of the most widely used CAD tools include:
-
AutoCAD – Industry standard for 2D and 3D drafting
-
Fusion 360 – Cloud-based CAD/CAM/CAE solution
-
SolidWorks – Powerful parametric 3D modeling tool
-
CATIA – Advanced CAD used in aerospace and automotive industries
-
FreeCAD – Open-source CAD software for parametric modeling
Each tool serves different needs, from beginners to advanced professionals.
CAD Skills and Career Opportunities
Learning CAD opens doors to a wide range of career paths, including:
-
CAD Designer
-
Mechanical Engineer
-
Product Designer
-
Architectural Draftsman
-
Manufacturing Engineer
-
Industrial Designer
With industries rapidly adopting automation and digital manufacturing, CAD professionals are in high demand globally.
Future of CAD Technology
The future of Computer-Aided Design is driven by innovation and integration with emerging technologies:
-
AI-powered design automation
-
Cloud-based collaborative CAD
-
Generative design
-
AR/VR visualization
-
Digital twins
These advancements will make CAD smarter, faster, and more intuitive, reducing human effort while increasing creativity and efficiency.
Conclusion
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) has become the backbone of modern design and engineering. From simple drawings to complex 3D simulations, CAD empowers professionals to design better, faster, and smarter. Whether you are a student, engineer, architect, or designer, mastering CAD is no longer optional—it is essential.
As technology evolves, CAD will continue to shape the future of innovation, manufacturing, and digital design. Investing time in learning CAD today can lead to limitless opportunities tomorrow.