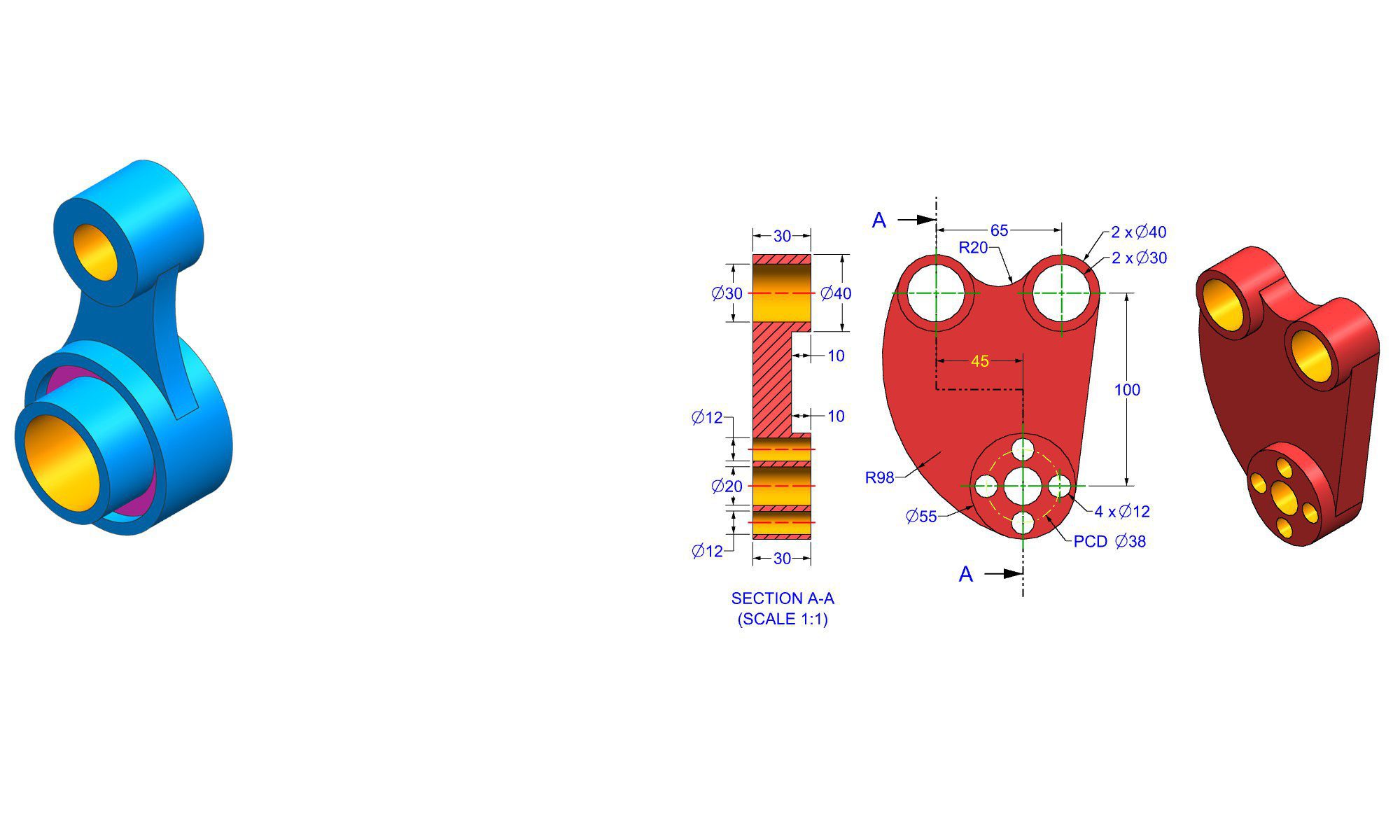
Fusion 360: The Complete Guide to Autodesk’s Cloud-Based CAD Software
Fusion 360 is one of the most advanced and versatile design tools available today. Developed by Autodesk, Fusion 360 combines CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) into a single cloud-based platform. This unified approach has made Fusion 360 a favorite among engineers, product designers, startups, and manufacturers worldwide.
In this guide, we’ll explore what Fusion 360 is, its key features, benefits, applications, and why it stands out in the modern CAD landscape.
What Is Fusion 360?
Fusion 360 is a professional 3D design and engineering software developed by Autodesk. Unlike traditional desktop-only CAD tools, Fusion 360 operates on a cloud-connected environment, enabling real-time collaboration, automatic updates, and secure data storage.
Fusion 360 supports:
-
3D parametric modeling
-
Freeform and surface modeling
-
Mechanical assemblies
-
Simulation and analysis
-
CNC machining and manufacturing workflows
This all-in-one approach eliminates the need for multiple disconnected tools.
Key Features of Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is packed with powerful features designed for modern product development.
1. Parametric and Direct Modeling
Fusion 360 allows both parametric modeling (dimension-driven designs) and direct modeling for flexible edits. Designers can quickly iterate without breaking design intent.
2. Cloud-Based Collaboration
All projects are stored securely in the cloud, allowing teams to:
-
Collaborate in real time
-
Track design history
-
Access designs from anywhere
3. Integrated CAM
Fusion 360 includes built-in CAM tools for:
-
CNC milling
-
Turning
-
Cutting
-
Additive manufacturing
This makes it ideal for manufacturing-ready designs.
4. Simulation and Analysis (CAE)
Engineers can test designs using:
-
Stress and strain analysis
-
Thermal simulations
-
Motion studies
Early testing helps reduce design failures and production costs.
5. Generative Design
Fusion 360 uses AI-driven generative design to automatically create optimized design options based on materials, constraints, and manufacturing methods.
Benefits of Using Fusion 360
Fusion 360 offers several advantages over traditional CAD software.
Faster Product Development
By combining CAD, CAM, and CAE in one platform, Fusion 360 reduces workflow complexity and speeds up development cycles.
Cost-Effective Solution
Fusion 360 is more affordable than many high-end CAD tools and offers flexible subscription plans for startups, students, and hobbyists.
Easy Learning Curve
With an intuitive interface and extensive tutorials, Fusion 360 is beginner-friendly while still powerful enough for professionals.
Automatic Updates
Users always have access to the latest features without manual upgrades.
Applications of Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is used across a wide range of industries.
Product Design and Prototyping
Designers create functional prototypes and test them digitally before physical production.
Mechanical Engineering
Engineers design complex mechanical parts and assemblies with precision.
Manufacturing and CNC Machining
Fusion 360’s CAM tools generate toolpaths directly from CAD models, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
Electronics Design
Fusion 360 supports PCB design and integrates electronic and mechanical workflows.
Education and Training
Students and educators use Fusion 360 to learn modern design and manufacturing processes.
Fusion 360 vs Traditional CAD Software
Fusion 360 differs from traditional CAD tools in several ways:
-
Cloud-based collaboration instead of local file storage
-
Integrated manufacturing tools instead of third-party plugins
-
Subscription-based pricing instead of expensive perpetual licenses
-
Continuous feature updates instead of yearly releases
These advantages make Fusion 360 especially appealing to modern design teams.
Fusion 360 Pricing Overview
Fusion 360 offers multiple licensing options:
-
Free licenses for students, educators, and personal use
-
Commercial subscriptions for professionals and businesses
-
Startup plans with reduced pricing
This flexible pricing makes Fusion 360 accessible to users at all levels.
Future of Fusion 360
Autodesk continues to enhance Fusion 360 with:
-
AI-assisted design tools
-
Advanced generative design
-
Improved cloud performance
-
Deeper manufacturing integrations
As digital manufacturing and Industry 4.0 grow, Fusion 360 is positioned to remain a leading design platform.
Final Thoughts
Fusion 360 is more than just CAD software—it’s a complete product development ecosystem. By integrating design, engineering, and manufacturing into a single cloud-based platform, Fusion 360 empowers teams to innovate faster and smarter.
Whether you’re a student, startup founder, or professional engineer, Fusion 360 offers the tools needed to turn idea
End of Blog

CAD EXERCISES All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master CAD Through Real-World Practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills using any CAD software.Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is designed to help you gain real design confidence through structured, practice-oriented exercises.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide
Updated Blog Twelth Time
This is sample HTML content for the blog post.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Complete Guide to Modern CAD Software in 2026
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): A Complete Guide to Modern CAD Software
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is one of the most important technologies in modern engineering, architecture, and product development. From designing simple mechanical parts to creating complex architectural structures and advanced aerospace components, CAD software has revolutionized the way ideas are visualized, tested, and manufactured.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what CAD is, how it works, its benefits, major applications, and the best CAD software available today.
What Is Computer-Aided Design (CAD)?
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) refers to the use of computer software to create, modify, analyze, and optimize designs. CAD replaces traditional manual drafting with digital models, allowing designers to work faster, more accurately, and with greater flexibility.
CAD designs can be:
-
2D drawings (floor plans, schematics, technical drawings)
-
3D models (solid models, assemblies, surface designs)
Modern CAD tools support parametric modeling, simulation, rendering, and direct integration with manufacturing processes.
Why CAD Software Is Essential Today
CAD software has become an industry standard because it offers significant advantages over manual design methods.
Key Benefits of CAD
-
High Accuracy and Precision
CAD eliminates human measurement errors and ensures exact dimensions. -
Faster Design Process
Designs can be modified instantly without redrawing from scratch. -
Better Visualization
3D models help stakeholders understand designs before production. -
Easy Collaboration
CAD files can be shared globally, improving teamwork and version control. -
Cost Reduction
Early error detection reduces manufacturing and material waste.
Types of CAD Software
CAD software can be categorized based on industry and functionality.
1. 2D CAD Software
Used mainly for drafting and documentation.
-
Examples: AutoCAD (2D), LibreCAD
2. 3D CAD Software
Used for modeling real-world objects and assemblies.
-
Examples: SolidWorks, Fusion 360, FreeCAD
3. Parametric CAD
Allows changes by modifying parameters and constraints.
-
Ideal for mechanical and product design
4. Direct Modeling CAD
Allows free-form geometry editing without constraints.
-
Useful for concept design and quick iterations
Applications of CAD Across Industries
Engineering and Manufacturing
Mechanical engineers use CAD to design parts, assemblies, and tools. CAD integrates with CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) to produce CNC-ready models.
Architecture and Construction
Architects rely on CAD for floor plans, elevations, and 3D building models. It helps visualize spaces and comply with regulations.
Product Design
Industrial designers use CAD to prototype consumer products, electronics, and furniture with realistic materials and dimensions.
Automotive and Aerospace
CAD plays a critical role in vehicle and aircraft design, ensuring safety, performance, and aerodynamic efficiency.
Education and Research
Students and researchers use CAD to learn design principles and experiment with virtual models.
Best CAD Software in 2026
Here are some of the most popular and powerful CAD tools used today:
AutoCAD
-
Industry standard for 2D and 3D drafting
-
Widely used in architecture and engineering
SolidWorks
-
Excellent for mechanical and parametric modeling
-
Strong simulation and assembly tools
Fusion 360
-
Cloud-based CAD with CAM and CAE integration
-
Ideal for startups and product designers
FreeCAD
-
Open-source and free
-
Best for beginners and budget-conscious professionals
CATIA
-
Advanced CAD for aerospace and automotive industries
-
High-end surface modeling capabilities
CAD and the Future of Design
CAD technology continues to evolve rapidly. Some emerging trends include:
-
Cloud-based CAD for real-time collaboration
-
AI-assisted design for automated optimization
-
Generative design to explore multiple design solutions
-
AR/VR integration for immersive design reviews
-
Seamless CAD-to-3D-printing workflows
These innovations are making CAD more powerful, accessible, and intelligent than ever before.
How to Choose the Right CAD Software
When selecting CAD software, consider:
-
Your industry and use case
-
Required features (2D, 3D, simulation, rendering)
-
Budget and licensing model
-
Learning curve and community support
-
Compatibility with other tools
For beginners, free or affordable tools like FreeCAD or Fusion 360 are excellent starting points. Professionals may prefer industry-standard solutions like SolidWorks or AutoCAD.
Final Thoughts
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is the backbone of modern design and manufacturing. Whether you’re an engineer, architect, student, or product designer, mastering CAD software opens doors to innovation, efficiency, and career growth.
As industries continue to adopt digital workflows, CAD skills will remain in high demand. Investing time in learning the right CAD tools today can significantly impact your professional future.

After purchasing, a download link will be sent instantly to your email.
Are you a student or financially struggling? Get this bundle for $19.99
Offer for Students Buy Now For $19.99
Buy Paperback on Amazon.com
CAD EXERCISES All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master CAD Through Real-World Practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills using any CAD software.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry andtechnical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): Complete Guide to Modern CAD Software in 2026
Computer-Aided Design (CAD): A Complete Guide to Modern CAD Software
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is one of the most important technologies in modern engineering, architecture, and product development. From designing simple mechanical parts to creating complex architectural structures and advanced aerospace components, CAD software has revolutionized the way ideas are visualized, tested, and manufactured.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what CAD is, how it works, its benefits, major applications, and the best CAD software available today.
What Is Computer-Aided Design (CAD)?
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) refers to the use of computer software to create, modify, analyze, and optimize designs. CAD replaces traditional manual drafting with digital models, allowing designers to work faster, more accurately, and with greater flexibility.
CAD designs can be:
-
2D drawings (floor plans, schematics, technical drawings)
-
3D models (solid models, assemblies, surface designs)
Modern CAD tools support parametric modeling, simulation, rendering, and direct integration with manufacturing processes.
Why CAD Software Is Essential Today
CAD software has become an industry standard because it offers significant advantages over manual design methods.
Key Benefits of CAD
-
High Accuracy and Precision
CAD eliminates human measurement errors and ensures exact dimensions. -
Faster Design Process
Designs can be modified instantly without redrawing from scratch. -
Better Visualization
3D models help stakeholders understand designs before production. -
Easy Collaboration
CAD files can be shared globally, improving teamwork and version control. -
Cost Reduction
Early error detection reduces manufacturing and material waste.
Types of CAD Software
CAD software can be categorized based on industry and functionality.
1. 2D CAD Software
Used mainly for drafting and documentation.
-
Examples: AutoCAD (2D), LibreCAD
2. 3D CAD Software
Used for modeling real-world objects and assemblies.
-
Examples: SolidWorks, Fusion 360, FreeCAD
3. Parametric CAD
Allows changes by modifying parameters and constraints.
-
Ideal for mechanical and product design
4. Direct Modeling CAD
Allows free-form geometry editing without constraints.
-
Useful for concept design and quick iterations
Applications of CAD Across Industries
Engineering and Manufacturing
Mechanical engineers use CAD to design parts, assemblies, and tools. CAD integrates with CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) to produce CNC-ready models.
Architecture and Construction
Architects rely on CAD for floor plans, elevations, and 3D building models. It helps visualize spaces and comply with regulations.
Product Design
Industrial designers use CAD to prototype consumer products, electronics, and furniture with realistic materials and dimensions.
Automotive and Aerospace
CAD plays a critical role in vehicle and aircraft design, ensuring safety, performance, and aerodynamic efficiency.
Education and Research
Students and researchers use CAD to learn design principles and experiment with virtual models.
Best CAD Software in 2026
Here are some of the most popular and powerful CAD tools used today:
AutoCAD
-
Industry standard for 2D and 3D drafting
-
Widely used in architecture and engineering
SolidWorks
-
Excellent for mechanical and parametric modeling
-
Strong simulation and assembly tools
Fusion 360
-
Cloud-based CAD with CAM and CAE integration
-
Ideal for startups and product designers
FreeCAD
-
Open-source and free
-
Best for beginners and budget-conscious professionals
CATIA
-
Advanced CAD for aerospace and automotive industries
-
High-end surface modeling capabilities
CAD and the Future of Design
CAD technology continues to evolve rapidly. Some emerging trends include:
-
Cloud-based CAD for real-time collaboration
-
AI-assisted design for automated optimization
-
Generative design to explore multiple design solutions
-
AR/VR integration for immersive design reviews
-
Seamless CAD-to-3D-printing workflows
These innovations are making CAD more powerful, accessible, and intelligent than ever before.
How to Choose the Right CAD Software
When selecting CAD software, consider:
-
Your industry and use case
-
Required features (2D, 3D, simulation, rendering)
-
Budget and licensing model
-
Learning curve and community support
-
Compatibility with other tools
For beginners, free or affordable tools like FreeCAD or Fusion 360 are excellent starting points. Professionals may prefer industry-standard solutions like SolidWorks or AutoCAD.
Final Thoughts
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is the backbone of modern design and manufacturing. Whether you’re an engineer, architect, student, or product designer, mastering CAD software opens doors to innovation, efficiency, and career growth.
As industries continue to adopt digital workflows, CAD skills will remain in high demand. Investing time in learning the right CAD tools today can significantly impact your professional future.
End of Blog

CAD EXERCISES All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master CAD Through Real-World Practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills using any CADsoftware.Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is designed to help you gain real design confidence through structured, practice-oriented exercises.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide