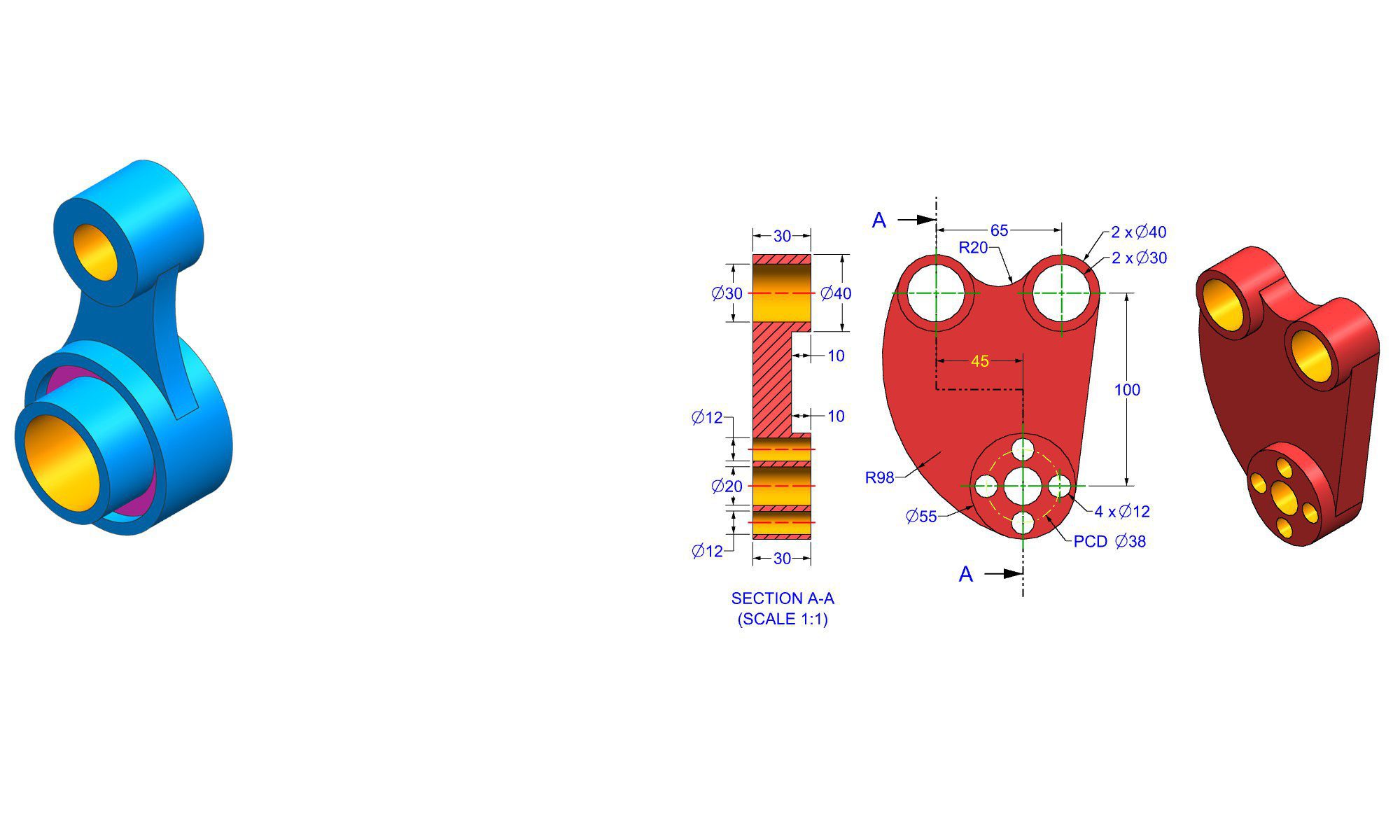
Introduction
FreeCAD, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360 are three of the most popular computer-aided design (CAD) software tools available on the market. Each of these tools has its unique features, advantages, and disadvantages, making it essential to choose the right one for your specific needs. In this article, we will delve into the world of CAD software and compare FreeCAD, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360 to help you decide which one is the best fit for you.
Key Features and Differences
Before we dive into the comparison, let’s take a look at the key features and differences between these three CAD software tools.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is an open-source CAD software that is available for free. It is a 3D CAD modeler and parametric design tool that supports several workbenches, including the Part Design, Assembly, and Drawing workbenches. FreeCAD is ideal for those who want to create complex 3D models, but it may not be the best option for those who are new to CAD software.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a commercial CAD software developed by Autodesk. It is one of the most widely used CAD software tools in the industry and is known for its powerful features and user-friendly interface. AutoCAD is ideal for architects, engineers, and designers who need to create accurate and detailed 2D and 3D models.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based CAD software developed by Autodesk. It is a 3D CAD modeler and parametric design tool that supports several features, including CAD, CAM, and CAE. Fusion 360 is ideal for those who want to create complex 3D models and need to collaborate with others in real-time.
When it comes to performance and ease of use, each of these CAD software tools has its strengths and weaknesses.
FreeCAD is a resource-intensive software that may not perform well on older computers. However, it is free and open-source, making it an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. AutoCAD is a powerful software that can handle large and complex models, but it may require a powerful computer to run smoothly. Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that can be accessed from anywhere, making it an excellent option for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time.
Ease of Use
FreeCAD has a steeper learning curve than AutoCAD and Fusion 360, but it offers a wide range of tutorials and documentation to help users get started. AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. Fusion 360 is also relatively easy to use, especially for those who are familiar with CAD software.
Cost and Licensing
When it comes to cost and licensing, each of these CAD software tools has its unique pricing model.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is free and open-source, making it an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. However, it may require a one-time donation to support the development of the software.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a commercial software that requires a license to use. The cost of AutoCAD depends on the edition and the number of users. The most basic edition, AutoCAD LT, costs around $1,500 per year, while the most advanced edition, AutoCAD Ultimate, costs around $4,000 per year.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that offers a free version for hobbyists and startups. The free version includes many features, including CAD, CAM, and CAE. However, it may not be suitable for commercial use. The paid version of Fusion 360 costs around $40 per month, or $30 per month for a year.
Compatibility and Integration
When it comes to compatibility and integration, each of these CAD software tools has its unique strengths and weaknesses.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is compatible with several file formats, including STEP, IGES, and STL. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is compatible with several file formats, including DWG, DXF, and STEP. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is compatible with several file formats, including STL, OBJ, and IGES. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CAD software tool depends on your specific needs and requirements. FreeCAD is an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that is ideal for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time. Ultimately, the choice between these three CAD software tools depends on your specific needs and requirements.
FAQ
What is the difference between FreeCAD and AutoCAD?
FreeCAD is an open-source CAD software that is available for free, while AutoCAD is a commercial software that requires a license to use. AutoCAD is more powerful and user-friendly than FreeCAD, but it may not be suitable for those who are on a budget.
Is Fusion 360 free?
Fusion 360 offers a free version for hobbyists and startups, but it may not be suitable for commercial use. The paid version of Fusion 360 costs around $40 per month, or $30 per month for a year.
FreeCAD is compatible with several file formats, including STEP, IGES, and STL. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Is AutoCAD suitable for beginners?
Yes, AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. It offers a wide range of tutorials and documentation to help users get started.
Can I access Fusion 360 from anywhere?
Yes, Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that can be accessed from anywhere. It is ideal for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time.
Fusion 360 is compatible with several file formats, including STL, OBJ, and IGES. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Is FreeCAD available for Windows, Mac, and Linux?
Yes, FreeCAD is available for Windows, Mac, and Linux. It is a free and open-source software that can be downloaded from the official website.
AutoCAD is compatible with several software tools, including Microsoft Office and Google Docs. However, it may not be compatible with all software tools, especially those from other CAD software vendors.
End of Blog
FREECAD All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master FreeCAD through real-world practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills with FreeCAD. Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is built to help you gain real design confidence through structured practice.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide

Introduction
FreeCAD is an open-source 3D computer-aided design (CAD) software that offers a range of tools for modeling and designing various objects, from simple household items to complex machines. While FreeCAD is primarily designed for 3D modeling, it also includes a powerful 2D drafting module that allows users to create precise and accurate 2D drawings. In this step-by-step guide, we will explore the process of 2D drafting in FreeCAD, covering the basics and advanced techniques to help you get started.
Setting Up the 2D Workbench
To begin 2D drafting in FreeCAD, you need to switch to the Draft Workbench. This workbench provides a set of tools specifically designed for 2D drafting. To access the Draft Workbench, follow these steps:
- Open FreeCAD and create a new project.
- Click on the “Workbench” menu at the top of the screen and select “Draft” from the drop-down list.
- You should now see the Draft Workbench toolbar and menu.
Creating a New 2D Document
Before you can start drafting, you need to create a new 2D document. To do this, follow these steps:
- Click on the “File” menu and select “New” from the drop-down list.
- In the “Create new document” dialog box, select “Draft” as the document type.
- Choose a document name and location, and click “OK.”
Drawing Basic Shapes
Once you have created a new 2D document, you can start drawing basic shapes using the Draft Workbench tools. Here are the steps to draw a rectangle, circle, and line:
Drawing a Rectangle
- Select the “Rectangle” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Click on the screen where you want to place the top-left corner of the rectangle.
- Drag the mouse to define the size and position of the rectangle.
- Release the mouse button to create the rectangle.
Drawing a Circle
- Select the “Circle” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Click on the screen where you want to place the center of the circle.
- Drag the mouse to define the radius of the circle.
- Release the mouse button to create the circle.
Drawing a Line
- Select the “Line” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Click on the screen where you want to place the start point of the line.
- Drag the mouse to define the direction and length of the line.
- Release the mouse button to create the line.
Modifying and Manipulating Shapes
Once you have created basic shapes, you can modify and manipulate them using the Draft Workbench tools. Here are some common operations:
Moving a Shape
- Select the shape you want to move.
- Click on the “Move” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Click on the screen where you want to move the shape to.
- Release the mouse button to move the shape.
Scaling a Shape
- Select the shape you want to scale.
- Click on the “Scale” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Click on the screen where you want to scale the shape from.
- Drag the mouse to define the scaling factor.
- Release the mouse button to scale the shape.
Rotating a Shape
- Select the shape you want to rotate.
- Click on the “Rotate” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Click on the screen where you want to rotate the shape from.
- Drag the mouse to define the rotation angle.
- Release the mouse button to rotate the shape.
Working with Dimensions and Constraints
Dimensions and constraints are essential for creating accurate and reliable 2D drawings. Here are some tips for working with dimensions and constraints in FreeCAD:
Adding Dimensions
- Select the shape you want to add a dimension to.
- Click on the “Dimension” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Click on the screen where you want to place the dimension.
- Choose the dimension type (e.g., length, angle, radius) and click “OK.”
Adding Constraints
- Select the shape you want to add a constraint to.
- Click on the “Constraint” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar.
- Choose the constraint type (e.g., fixed, coincident, perpendicular) and click “OK.”
Exporting and Printing 2D Drawings
Once you have completed your 2D drawing, you can export it as a vector file (e.g., PDF, SVG) or print it directly from FreeCAD. Here are the steps to export and print a 2D drawing:
Exporting a 2D Drawing
- Select the 2D drawing you want to export.
- Click on the “File” menu and select “Export” from the drop-down list.
- Choose the file format (e.g., PDF, SVG) and location, and click “OK.”
Printing a 2D Drawing
- Select the 2D drawing you want to print.
- Click on the “File” menu and select “Print” from the drop-down list.
- Choose the printer and paper settings, and click “OK.”
Conclusion
FreeCAD’s 2D drafting module offers a powerful and flexible set of tools for creating accurate and reliable 2D drawings. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can master the basics of 2D drafting in FreeCAD and start creating professional-looking drawings.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between FreeCAD’s 2D and 3D drafting modules?
A: FreeCAD’s 2D drafting module is specifically designed for creating 2D drawings, while the 3D drafting module is designed for creating 3D models.
Q: Can I use FreeCAD to draw architectural plans?
A: Yes, FreeCAD can be used to draw architectural plans, including floor plans, elevations, and cross-sections.
Q: How do I add text to a 2D drawing in FreeCAD?
A: To add text to a 2D drawing in FreeCAD, select the “Text” tool from the Draft Workbench toolbar and click on the screen where you want to place the text.
Q: Can I use FreeCAD to create technical drawings?
A: Yes, FreeCAD can be used to create technical drawings, including schematics, diagrams, and blueprints.
Q: How do I import a 2D drawing into FreeCAD?
A: To import a 2D drawing into FreeCAD, click on the “File” menu and select “Import” from the drop-down list.
Q: Can I use FreeCAD to create 2D animations?
A: Yes, FreeCAD can be used to create 2D animations, including GIFs and videos.
Q: How do I create a new 2D template in FreeCAD?
A: To create a new 2D template in FreeCAD, click on the “File” menu and select “New” from the drop-down list, then select “Draft” as the document type.
End of Blog
FREECAD All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master FreeCAD through real-world practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills with FreeCAD. Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is built to help you gain real design confidence through structured practice.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide

Introduction
FreeCAD is a powerful, open-source 3D computer-aided design (CAD) software that has gained popularity among makers, hobbyists, and professionals alike. One of its notable features is its ability to seamlessly integrate with 3D printing technology, making it an excellent choice for creating and printing complex designs. In this article, we’ll delve into the best practices for using FreeCAD for 3D printing, covering essential topics such as design principles, modeling techniques, and post-processing tips.
Setting Up FreeCAD for 3D Printing
Before diving into the world of 3D printing with FreeCAD, it’s essential to set up the software correctly. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
Installing FreeCAD
To begin, download the latest version of FreeCAD from the official website. The software is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms. Once downloaded, follow the installation instructions for your operating system.
Configuring FreeCAD for 3D Printing
After installation, launch FreeCAD and navigate to “Settings” > “Configure” > “General.” In the “Default Units” section, set the units to “mm” (millimeters) to ensure accurate measurements for 3D printing. Additionally, set the “Precision” to “4” to achieve the desired level of detail in your designs.
Design Principles for 3D Printing
When designing for 3D printing, it’s crucial to follow certain principles to ensure successful prints. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
Understanding 3D Printing Terminology
Before diving into design, familiarize yourself with basic 3D printing terminology. Key terms include:
- Infill: The internal structure of a 3D printed object, which can be adjusted to reduce weight or increase strength.
- Perimeter: The outer boundary of a 3D printed object, which can be adjusted to change the object’s appearance.
- Shell: The outer layer of a 3D printed object, which can be adjusted to change the object’s thickness.
Designing for 3D Printing
When designing for 3D printing, consider the following factors:
- Resolution: The level of detail in your design, which can be affected by the 3D printer’s resolution and layer height.
- Support material: The material used to support overhanging features or complex geometries, which can be adjusted to reduce waste and improve print quality.
- Orientation: The way your design is oriented on the print bed, which can affect print quality, warping, and adhesion.
Modeling Techniques for 3D Printing
FreeCAD offers a range of modeling techniques that can help you create complex designs for 3D printing. Here are some essential techniques to master:
Working with Primitives
FreeCAD’s primitive shapes (e.g., cubes, spheres, cylinders) can be combined to create complex designs. Use the “Part” workbench to manipulate and combine primitive shapes.
Using the Part Design Workbench
The Part Design workbench allows you to create custom shapes using parametric modeling. Use this workbench to create complex geometries, such as holes, slots, and chamfers.
Applying Materials and Finishes
FreeCAD allows you to apply materials and finishes to your designs, simulating real-world materials and effects. Use this feature to visualize your designs in various materials and finishes.
Post-Processing Tips for 3D Printing
After printing, it’s essential to post-process your designs to achieve the desired finish and quality. Here are some essential tips to follow:
Sanding and Smoothing
Use a sanding block or a Dremel tool to smooth out rough edges and surfaces. Apply a coat of primer or paint to enhance the finish.
Removing Support Material
Use a hobby knife or a razor blade to carefully remove support material from your design. Be gentle to avoid damaging the surrounding material.
Applying Finishing Coats
Apply a clear coat or a paint to enhance the finish and protect the material from damage.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
As with any 3D printing software, you may encounter common issues that can be resolved by following these troubleshooting tips:
Issues with Infill
If your infill is not printing correctly, check the “Infill” settings in the “Settings” menu. Adjust the infill density and pattern to achieve the desired effect.
Issues with Support Material
If your support material is not printing correctly, check the “Support” settings in the “Settings” menu. Adjust the support material type and density to achieve the desired effect.
Issues with Orientation
If your object is not printing correctly due to orientation, try rotating the object by 90 degrees or using the “Mirror” feature to create a mirror image.
Conclusion
Using FreeCAD for 3D printing is an excellent way to create complex designs and prints with ease. By following the best practices outlined in this article, you’ll be well on your way to mastering the software and achieving professional-quality prints. Remember to experiment with different design principles, modeling techniques, and post-processing tips to push the boundaries of what’s possible with 3D printing.
FAQ
What is the best way to export a 3D model from FreeCAD for 3D printing?
Export your 3D model as an STL file using the “Export” feature in the “Part” workbench. This file format is widely supported by 3D printing software and slicers.
How do I create a custom 3D printing profile in FreeCAD?
To create a custom 3D printing profile, navigate to “Settings” > “Configure” > “Add Printer.” Select the 3D printer model and follow the on-screen instructions to configure the profile.
Can I use FreeCAD for other applications besides 3D printing?
Yes, FreeCAD is a versatile CAD software that can be used for various applications, including architectural design, mechanical engineering, and product design.
How do I troubleshoot issues with my 3D prints?
Check the “Diagnostic” menu in the “Settings” menu to troubleshoot common issues with your 3D prints. You can also consult the FreeCAD community forums for help and support.
Can I use FreeCAD to create 3D models from scratch?
Yes, FreeCAD offers a range of tools and features to create 3D models from scratch. Use the “Part” workbench to create custom shapes and the “Part Design” workbench to create complex geometries.
Is FreeCAD free and open-source?
Yes, FreeCAD is a free and open-source CAD software that can be downloaded and used by anyone. The software is developed by a community of volunteers and contributors.
Introduction
FreeCAD, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360 are three of the most popular computer-aided design (CAD) software tools available on the market. Each of these tools has its unique features, advantages, and disadvantages, making it essential to choose the right one for your specific needs. In this article, we will delve into the world of CAD software and compare FreeCAD, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360 to help you decide which one is the best fit for you.
Key Features and Differences
Before we dive into the comparison, let’s take a look at the key features and differences between these three CAD software tools.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is an open-source CAD software that is available for free. It is a 3D CAD modeler and parametric design tool that supports several workbenches, including the Part Design, Assembly, and Drawing workbenches. FreeCAD is ideal for those who want to create complex 3D models, but it may not be the best option for those who are new to CAD software.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a commercial CAD software developed by Autodesk. It is one of the most widely used CAD software tools in the industry and is known for its powerful features and user-friendly interface. AutoCAD is ideal for architects, engineers, and designers who need to create accurate and detailed 2D and 3D models.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based CAD software developed by Autodesk. It is a 3D CAD modeler and parametric design tool that supports several features, including CAD, CAM, and CAE. Fusion 360 is ideal for those who want to create complex 3D models and need to collaborate with others in real-time.
When it comes to performance and ease of use, each of these CAD software tools has its strengths and weaknesses.
FreeCAD is a resource-intensive software that may not perform well on older computers. However, it is free and open-source, making it an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. AutoCAD is a powerful software that can handle large and complex models, but it may require a powerful computer to run smoothly. Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that can be accessed from anywhere, making it an excellent option for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time.
Ease of Use
FreeCAD has a steeper learning curve than AutoCAD and Fusion 360, but it offers a wide range of tutorials and documentation to help users get started. AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. Fusion 360 is also relatively easy to use, especially for those who are familiar with CAD software.
Cost and Licensing
When it comes to cost and licensing, each of these CAD software tools has its unique pricing model.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is free and open-source, making it an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. However, it may require a one-time donation to support the development of the software.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a commercial software that requires a license to use. The cost of AutoCAD depends on the edition and the number of users. The most basic edition, AutoCAD LT, costs around $1,500 per year, while the most advanced edition, AutoCAD Ultimate, costs around $4,000 per year.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that offers a free version for hobbyists and startups. The free version includes many features, including CAD, CAM, and CAE. However, it may not be suitable for commercial use. The paid version of Fusion 360 costs around $40 per month, or $30 per month for a year.
Compatibility and Integration
When it comes to compatibility and integration, each of these CAD software tools has its unique strengths and weaknesses.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is compatible with several file formats, including STEP, IGES, and STL. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is compatible with several file formats, including DWG, DXF, and STEP. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is compatible with several file formats, including STL, OBJ, and IGES. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CAD software tool depends on your specific needs and requirements. FreeCAD is an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that is ideal for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time. Ultimately, the choice between these three CAD software tools depends on your specific needs and requirements.
FAQ
What is the difference between FreeCAD and AutoCAD?
FreeCAD is an open-source CAD software that is available for free, while AutoCAD is a commercial software that requires a license to use. AutoCAD is more powerful and user-friendly than FreeCAD, but it may not be suitable for those who are on a budget.
Is Fusion 360 free?
Fusion 360 offers a free version for hobbyists and startups, but it may not be suitable for commercial use. The paid version of Fusion 360 costs around $40 per month, or $30 per month for a year.
FreeCAD is compatible with several file formats, including STEP, IGES, and STL. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Is AutoCAD suitable for beginners?
Yes, AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. It offers a wide range of tutorials and documentation to help users get started.
Can I access Fusion 360 from anywhere?
Yes, Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that can be accessed from anywhere. It is ideal for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time.
Fusion 360 is compatible with several file formats, including STL, OBJ, and IGES. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Is FreeCAD available for Windows, Mac, and Linux?
Yes, FreeCAD is available for Windows, Mac, and Linux. It is a free and open-source software that can be downloaded from the official website.
AutoCAD is compatible with several software tools, including Microsoft Office and Google Docs. However, it may not be compatible with all software tools, especially those from other CAD software vendors.
End of Blog
FREECAD All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master FreeCAD through real-world practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills with FreeCAD. Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is built to help you gain real design confidence through structured practice.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide
Introduction
FreeCAD, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360 are three of the most popular computer-aided design (CAD) software tools available on the market. Each of these tools has its unique features, advantages, and disadvantages, making it essential to choose the right one for your specific needs. In this article, we will delve into the world of CAD software and compare FreeCAD, AutoCAD, and Fusion 360 to help you decide which one is the best fit for you.
Key Features and Differences
Before we dive into the comparison, let’s take a look at the key features and differences between these three CAD software tools.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is an open-source CAD software that is available for free. It is a 3D CAD modeler and parametric design tool that supports several workbenches, including the Part Design, Assembly, and Drawing workbenches. FreeCAD is ideal for those who want to create complex 3D models, but it may not be the best option for those who are new to CAD software.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a commercial CAD software developed by Autodesk. It is one of the most widely used CAD software tools in the industry and is known for its powerful features and user-friendly interface. AutoCAD is ideal for architects, engineers, and designers who need to create accurate and detailed 2D and 3D models.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based CAD software developed by Autodesk. It is a 3D CAD modeler and parametric design tool that supports several features, including CAD, CAM, and CAE. Fusion 360 is ideal for those who want to create complex 3D models and need to collaborate with others in real-time.
When it comes to performance and ease of use, each of these CAD software tools has its strengths and weaknesses.
FreeCAD is a resource-intensive software that may not perform well on older computers. However, it is free and open-source, making it an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. AutoCAD is a powerful software that can handle large and complex models, but it may require a powerful computer to run smoothly. Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that can be accessed from anywhere, making it an excellent option for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time.
Ease of Use
FreeCAD has a steeper learning curve than AutoCAD and Fusion 360, but it offers a wide range of tutorials and documentation to help users get started. AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. Fusion 360 is also relatively easy to use, especially for those who are familiar with CAD software.
Cost and Licensing
When it comes to cost and licensing, each of these CAD software tools has its unique pricing model.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is free and open-source, making it an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. However, it may require a one-time donation to support the development of the software.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a commercial software that requires a license to use. The cost of AutoCAD depends on the edition and the number of users. The most basic edition, AutoCAD LT, costs around $1,500 per year, while the most advanced edition, AutoCAD Ultimate, costs around $4,000 per year.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that offers a free version for hobbyists and startups. The free version includes many features, including CAD, CAM, and CAE. However, it may not be suitable for commercial use. The paid version of Fusion 360 costs around $40 per month, or $30 per month for a year.
Compatibility and Integration
When it comes to compatibility and integration, each of these CAD software tools has its unique strengths and weaknesses.
FreeCAD
FreeCAD is compatible with several file formats, including STEP, IGES, and STL. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is compatible with several file formats, including DWG, DXF, and STEP. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Fusion 360
Fusion 360 is compatible with several file formats, including STL, OBJ, and IGES. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CAD software tool depends on your specific needs and requirements. FreeCAD is an excellent option for those who want to create complex 3D models without breaking the bank. AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that is ideal for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time. Ultimately, the choice between these three CAD software tools depends on your specific needs and requirements.
FAQ
What is the difference between FreeCAD and AutoCAD?
FreeCAD is an open-source CAD software that is available for free, while AutoCAD is a commercial software that requires a license to use. AutoCAD is more powerful and user-friendly than FreeCAD, but it may not be suitable for those who are on a budget.
Is Fusion 360 free?
Fusion 360 offers a free version for hobbyists and startups, but it may not be suitable for commercial use. The paid version of Fusion 360 costs around $40 per month, or $30 per month for a year.
FreeCAD is compatible with several file formats, including STEP, IGES, and STL. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Is AutoCAD suitable for beginners?
Yes, AutoCAD is a user-friendly software that is ideal for those who are new to CAD software. It offers a wide range of tutorials and documentation to help users get started.
Can I access Fusion 360 from anywhere?
Yes, Fusion 360 is a cloud-based software that can be accessed from anywhere. It is ideal for those who need to collaborate with others in real-time.
Fusion 360 is compatible with several file formats, including STL, OBJ, and IGES. However, it may not be compatible with all file formats, especially those from other CAD software tools.
Is FreeCAD available for Windows, Mac, and Linux?
Yes, FreeCAD is available for Windows, Mac, and Linux. It is a free and open-source software that can be downloaded from the official website.
AutoCAD is compatible with several software tools, including Microsoft Office and Google Docs. However, it may not be compatible with all software tools, especially those from other CAD software vendors.
End of Blog
FREECAD All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master FreeCAD through real-world practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills with FreeCAD. Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is built to help you gain real design confidence through structured practice.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide

Design Mechanical Parts in Minutes with FreeCAD: A Beginner’s Guide
FreeCAD is one of the most powerful open-source CAD tools available today—and the best part? You can start designing mechanical parts in just minutes, even if you’re a complete beginner.
This step-by-step guide will walk you through the fastest, simplest way to design mechanical parts in FreeCAD, without overwhelming you with advanced theory. If you want practical results quickly, this guide is for you.
Table of Contents
-
What Is FreeCAD and Why Use It for Mechanical Design
-
Installing and Setting Up FreeCAD
-
Understanding the FreeCAD Interface
-
Essential Workbenches for Beginners
-
Creating Your First Mechanical Part
-
Sketching Basics Every Beginner Must Know
-
Turning Sketches into 3D Solids
-
Modifying Designs with Parametric Modeling
-
Exporting Your Mechanical Part
-
Common Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
-
Final Thoughts
1. What Is FreeCAD and Why Use It for Mechanical Design
FreeCAD is a parametric 3D CAD software widely used for:
-
Mechanical part design
-
Product prototyping
-
Engineering projects
-
3D printing
Why Beginners Love FreeCAD
-
100% free and open source
-
No licensing restrictions
-
Parametric design makes edits easy
-
Active community and frequent updates
Unlike traditional CAD tools, FreeCAD lets you change dimensions at any time, and the entire model updates automatically.
2. Installing and Setting Up FreeCAD
Download FreeCAD from the official website and install it for your operating system.
Recommended Initial Settings
-
Set units to Millimeters (mm)
-
Enable Auto Constraints in Sketcher
-
Switch navigation style to CAD mode
These small setup steps help you work faster right from day one.
3. Understanding the FreeCAD Interface
At first glance, FreeCAD can look complex—but it’s highly logical.
Key Interface Elements
-
Workbenches – Toolsets for specific tasks
-
Combo View – Model tree and properties
-
3D View – Your design workspace
💡 Tip: Focus on one workbench at a time to avoid confusion.
4. Essential Workbenches for Beginners
You don’t need all of FreeCAD to get started.
Start with These:
-
Sketcher – Create 2D sketches
-
Part Design – Convert sketches into 3D parts
-
TechDraw – Create 2D drawings (later)
Mastering just Sketcher and Part Design allows you to create 90% of common mechanical parts.
5. Creating Your First Mechanical Part
Let’s design a simple mechanical plate.
Step-by-Step Overview
-
Switch to Part Design
-
Create a New Body
-
Start a New Sketch
-
Choose a reference plane (XY Plane)
-
Draw a rectangle
This is the foundation of nearly every mechanical component.
6. Sketching Basics Every Beginner Must Know
Sketches define your part—clean sketches mean faster modeling.
Best Practices
-
Always fully constrain sketches
-
Use dimensional constraints instead of guessing
-
Avoid unnecessary geometry
A fully constrained sketch turns green—this ensures stability.
7. Turning Sketches into 3D Solids
Once your sketch is ready:
Example:
In seconds, your 2D sketch becomes a functional 3D mechanical part.
8. Modifying Designs with Parametric Modeling
This is where FreeCAD truly shines.
Change Once, Update Everywhere
-
Edit sketch dimensions
-
Adjust pad lengths
-
Modify hole diameters
The entire model updates automatically—no need to start over.
This is perfect for:
9. Exporting Your Mechanical Part
Once your design is complete, you can export it easily.
Common Export Formats
FreeCAD supports nearly every industry-standard format.
10. Common Beginner Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid these to save time and frustration:
❌ Sketching without constraints
❌ Attaching sketches directly to faces
❌ Mixing multiple parts in one body
❌ Ignoring the model tree
✅ Use datum planes
✅ Name sketches and features
✅ Build step by step
11. Final Thoughts
Designing mechanical parts doesn’t have to be complicated.
With FreeCAD:
-
You can go from idea to 3D model in minutes
-
Beginners can learn without expensive software
-
Parametric design gives you full control
Start simple, practice daily, and FreeCAD will quickly become one of your most powerful design tools.
End of Blog
FREECAD All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master FreeCAD through real-world practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills with FreeCAD. Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is built to help you gain real design confidence through structured practice.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide

Boost FreeCAD Productivity: Expert Workflow Optimization Tips
FreeCAD is a powerful open-source CAD tool, but many users barely scratch the surface of its productivity potential. Whether you’re a mechanical designer, product engineer, or hobbyist maker, optimizing your FreeCAD workflow can save hours per project, reduce errors, and make modeling far more enjoyable.
In this guide, we’ll explore expert-level FreeCAD workflow optimization tips that help you work faster, smarter, and with confidence—without sacrificing precision.
Table of Contents
-
Why Workflow Optimization Matters in FreeCAD
-
Customize the FreeCAD Interface for Speed
-
Master Keyboard Shortcuts and Navigation
-
Build Robust Parametric Models
-
Use the Right Workbench at the Right Time
-
Sketcher Best Practices for Faster Modeling
-
Reuse Designs with Spreadsheets and Templates
-
Reduce Errors with Dependency Management
-
Performance Optimization for Large Projects
-
Final Thoughts: Work Smarter, Not Harder
1. Why Workflow Optimization Matters in FreeCAD
FreeCAD’s parametric modeling engine is incredibly flexible—but that flexibility can slow you down if your workflow isn’t structured.
Optimized workflows help you:
-
Minimize model rebuild failures
-
Make design changes in seconds instead of minutes
-
Collaborate more efficiently
-
Scale from simple parts to complex assemblies
Professionals don’t just “model”—they design with intent.
2. Customize the FreeCAD Interface for Speed
Hide What You Don’t Use
FreeCAD ships with many workbenches, but using all of them at once creates clutter.
Pro tips:
-
Disable unused workbenches via Tools → Customize
-
Keep only Part Design, Sketcher, and one auxiliary workbench visible
Create Custom Toolbars
If you repeatedly use tools like:
-
Pad
-
Pocket
-
Fillet
-
Datum Plane
Create a custom toolbar so your most-used tools are one click away.
3. Master Keyboard Shortcuts and Navigation
Keyboard shortcuts are one of the biggest productivity multipliers in FreeCAD.
Essential Shortcuts
-
Space → Toggle visibility
-
Ctrl + Z / Ctrl + Y → Undo / Redo
-
Ctrl + Click → Multi-select
-
Shift + Middle Mouse → Pan
-
Middle Mouse → Rotate view
💡 Expert Tip: Customize shortcuts for frequently used tools like Sketcher constraints to dramatically speed up sketching.
4. Build Robust Parametric Models
A fast workflow isn’t just about speed—it’s about stability.
Follow the “One Feature, One Purpose” Rule
Avoid stacking too many operations into a single sketch.
Instead:
Name Everything
Rename:
-
Sketches
-
Pads
-
Pockets
-
Datum planes
This makes your Model Tree readable, especially when revisiting old designs.
5. Use the Right Workbench at the Right Time
Many productivity issues come from using the wrong tool for the job.
Recommended Workflow
-
Sketcher + Part Design → Parametric solids
-
Part Workbench → Boolean operations
-
Draft Workbench → 2D references and construction geometry
-
TechDraw → Manufacturing drawings
Switching workbenches intentionally keeps your workflow clean and predictable.
6. Sketcher Best Practices for Faster Modeling
Sketches are the backbone of FreeCAD—optimize them, and everything speeds up.
Fully Constrain Every Sketch
Unconstrained sketches:
Use:
Avoid Redundant Constraints
Over-constraining increases solver time and leads to errors. Aim for just enough constraints, not more.
7. Reuse Designs with Spreadsheets and Templates
Drive Dimensions with Spreadsheets
The Spreadsheet Workbench lets you:
-
Control dimensions centrally
-
Create configurable designs
-
Reuse models for multiple variants
Example:
Create Project Templates
Save time by creating templates with:
-
Predefined units
-
Default workbenches
-
Common parameters
8. Reduce Errors with Dependency Management
FreeCAD follows a dependency chain—breaking it causes failures.
Avoid the Topological Naming Problem
Best practices:
-
Use Datum Planes instead of faces
-
Reference sketches, not generated geometry
-
Avoid attaching sketches directly to faces
These habits dramatically reduce model breakage during edits.
9. Performance Optimization for Large Projects
When working on complex designs:
Recommended Settings
-
Disable automatic recompute
-
Recompute manually after major changes
-
Simplify sketches and features
Use Lightweight Assemblies
If you’re assembling multiple parts:
This keeps FreeCAD responsive even on modest hardware.
10. Final Thoughts: Work Smarter, Not Harder
Boosting productivity in FreeCAD isn’t about rushing—it’s about intentional design, clean structure, and smart habits.
By:
-
Customizing your interface
-
Mastering Sketcher discipline
-
Using parametric tools effectively
You’ll spend less time fixing issues and more time creating great designs.
FreeCAD rewards those who think ahead—and with these expert workflow optimization tips, you’ll feel the difference immediately
End of Blog
FREECAD All-in-One Workbook
500+ Practice Exercises to Master FreeCAD through real-world practice!
This all-in-one workbook is your ultimate resource to develop hands-on CAD skills with FreeCAD. Whether you’re a student, engineer, hobbyist, or professional, this guide is built to help you gain real design confidence through structured practice.
What’s Inside this Book:
- 200 2D Sketching Exercises – Build a strong foundation in dimension-driven 2D geometry and technical drawings
- 200 3D Modeling Exercises – Practice modeling real-world parts, from simple shapes to complex components.
- Multi-Part Assembly Projects – Understand how parts fit together and create full assemblies with detailed drawings
🎯 Why This Book?
- 500+ practice exercises following real design standards
- Designed for self-paced learning & independent practice
- Perfect for classrooms, technical interview preparation, and personal projects
- Covers 2D Sketching, 3D Modeling & Assembly Design in one workbook
- Trusted by 15,000+ CAD learners worldwide